Rainwater Harvesting: Sustainable Water Solutions for Urban and Rural Communities
Rainwater harvesting is a practical climate smart approach to reduce reliance on centralized water supplies and to build local resilience in both cities and rural regions. As pressure on freshwater resources grows due to population increases and changing rainfall patterns, systems that capture and store rainwater offer a reliable method to supplement drinking supply irrigation and industrial use while lowering utility costs and environmental impact. This article explains how rainwater harvesting works why it matters and how communities and businesses can implement effective systems.
Why Rainwater Harvesting Matters
Climate variability and aging water infrastructure create vulnerability for households and commercial operations. Rainwater harvesting helps address these challenges by collecting water at the point where it falls and making it available for many uses. Benefits include improved water security reduced storm water runoff that can cause erosion and pollution and lower demand on municipal treatment facilities. In addition to environmental gains harvesting rainwater can reduce water bills and support green building goals.
For readers seeking ongoing coverage of environmental innovation and local projects visit ecoglobalo.com for curated articles and best practice examples from around the world.
How Rainwater Harvesting Works
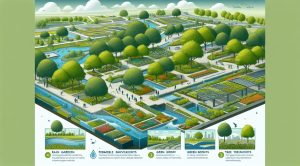
At its simplest rainwater harvesting involves four components. The first is the catchment surface which is often a roof that collects falling rain. The second is the conveyance system such as gutters and downspouts that channel water from the catchment to storage. The third is storage itself which can be above ground tanks or below ground cisterns sized according to needs and local rainfall patterns. The fourth is treatment and distribution which can range from basic filters for irrigation to more advanced filtration and disinfection when water is needed for human consumption.
Design choices depend on intended use. For garden watering minimal treatment is required while potable use requires careful filtration disinfection and sometimes ultraviolet treatment to meet health standards. Systems may also include first flush diverters which remove the initial dirty flow from the roof before water enters storage improving overall water quality.
Types of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Rainwater systems vary from simple barrel setups to integrated household systems connected to plumbing. Common options include barrel systems that are easy to install and ideal for gardening. Larger systems with tanks and pumps can supply toilets laundry and irrigation. Community scale systems collect large volumes for shared use in schools parks and public buildings. Each type has trade offs in cost complexity maintenance and the level of treatment required.
Designing an Effective System
Good design begins with understanding local rainfall patterns roof area and water demand. Calculating potential yield is straightforward by multiplying rainfall depth by catchment area and applying a runoff coefficient that reflects roof material. Storage should be sized to balance supply and demand ensuring there is capacity to capture heavy rainfall events while providing enough reserve during dry spells.
Placement of tanks should consider access for maintenance and secure connections to gutters. Materials range from plastic and fiberglass to concrete and metal. Each offers different durability cost and water quality characteristics. Pumps and controls must be selected for reliability and energy efficiency. Where electricity is unreliable solar powered pumps offer an effective solution.
Benefits for Homes Businesses and Communities
At the household level rainwater harvesting can cut potable water use for non drinking functions by a significant percentage. Homeowners find that captured water supports gardens reduces storm water fees and provides backup supply during service interruptions. For businesses and commercial properties investments in rainwater systems often yield rapid returns through reduced utility bills and improved sustainability reporting.
Community scale adoption amplifies benefits. Schools and public facilities that collect rainwater can reduce municipal storm water loads and showcase sustainable practices to visitors and students. Municipalities that promote rainwater harvesting through incentives or building code credits help scale adoption creating greener urban environments.
Entrepreneurs and service providers can find market opportunities in planning installation training and maintenance of rainwater systems. For a broader view on how businesses are engaging with environmental markets see research and discussion on BusinessForumHub.com which highlights case studies and strategies for growth in this sector.
Quality and Maintenance Considerations
Keeping harvested water safe and usable requires regular maintenance. Roofs and gutters should be inspected and cleaned seasonally to remove leaves debris and bird droppings. Tanks require periodic flushing and inspection for cracks contamination and insect entry. Filters and first flush devices need replacement or cleaning at recommended intervals.
Ensuring water quality involves appropriate treatment for intended use. Sediment filters charcoal filters and ultraviolet units each address different contaminants. When systems are used for drinking it is important to follow local health guidelines and testing requirements. Simple measures such as secure covers screens to prevent mosquito breeding and avoiding storage near chemical sources help reduce risk.
Overcoming Barriers to Adoption
Despite clear benefits there are barriers that slow adoption. Upfront cost uncertainty about regulations and lack of technical expertise can discourage homeowners and small businesses. Policy incentives rebates and streamlined permitting can accelerate uptake. Education programs that demonstrate cost savings and health protective measures help build trust.
Community pilot projects and demonstration sites can show real world performance and reduce perceived risk. Local governments can adopt supportive building codes and provide financial incentives to scale systems in public buildings and affordable housing projects. Where water tariffs reflect scarcity or where storm water fees are applied the economic case for rainwater harvesting becomes stronger.
Future Trends and Innovation
Technological advances are making systems smarter and more efficient. Internet connected sensors and controllers allow owners to monitor tank levels water quality and pump performance from a phone enabling proactive maintenance and improved water management. Integration with grey water recycling and landscape design for water efficient plants creates circular water strategies for properties.
Materials innovation and modular storage solutions reduce installation time and cost while community scale storage paired with green infrastructure such as rain gardens increases urban resilience to heavy rainfall events. Financing models that bundle installation with property upgrades and energy improvements can make rainwater systems more affordable and accessible.
Conclusion
Rainwater harvesting is a versatile tool in the wider suite of sustainable water management practices. Whether used to water gardens supply toilets support commercial operations or provide emergency reserves harvested rainwater reduces pressure on centralized systems lowers environmental impact and creates local benefits. With thoughtful design regular maintenance and supportive policies rainwater harvesting can play a central role in building resilient water systems for the future.
Implementing a rainwater system begins with assessment of needs and local conditions and can be scaled to match budget and goals. For continuous updates on environmental solutions and global projects visit our site to learn more about practical innovations and success stories.