Eco Design A Global Guide to Sustainable Creativity
Eco Design is rising as a central concept in architecture product creation and urban planning. As global societies face resource strain and climate change pressures designers and decision makers turn to Eco Design as a practical route to lower impact and greater value. This article explains what Eco Design means why it matters and how businesses governments and individuals can apply its principles to achieve measurable environmental and social benefits.
What Eco Design Means Today
Eco Design refers to the intentional process of designing products systems and spaces so they use fewer resources cause less pollution and last longer while delivering user value. Unlike older approaches that treated sustainability as an afterthought Eco Design embeds environmental thinking at the earliest stages of concept development. It covers material selection energy efficiency repairability reuse and end of life planning. It also addresses social factors such as fair labor practices and community well being.
Use of the phrase Eco Design signals a shift from single item thinking to system level solutions. For example a building is not just a collection of components but a living asset that should optimize energy flows water use and occupant health over decades. A household product is not just a thing to sell but a service that can be maintained upgraded and eventually recycled. This systems view helps reduce waste and create economic resilience.
Key Principles of Eco Design
There are core Eco Design principles that guide practical work across sectors. These principles help design teams make consistent decisions that align with larger climate goals.
– Minimize resource use by choosing materials and processes that require less energy and water to produce and to operate.
– Maximize durability and repairability so products remain useful longer and can be serviced rather than discarded.
– Favor renewable materials and low impact manufacturing to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and toxic outputs.
– Design for reuse and recycling so components have a clear path to be recovered and re processed at end of life.
– Optimize energy performance through passive strategies and efficient systems to lower operating demands.
– Consider the whole life cycle including extraction production distribution use and disposal to identify real environmental hotspots.
– Prioritize human health by avoiding toxic substances and improving indoor environmental quality.
Applying these core ideas creates products and places that perform well environmentally while meeting market needs.
Eco Design in Architecture and Urban Planning
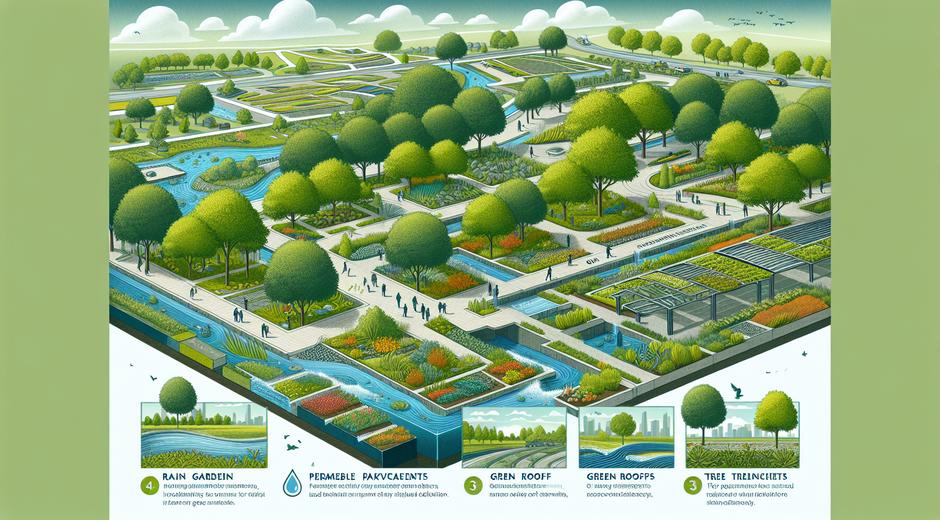
Architecture has become a powerful platform for Eco Design. Green building strategies extend beyond simple energy saving to include site selection water management materials choices and occupant wellness. Passive design choices such as building orientation natural ventilation shading and daylighting reduce dependence on mechanical systems. Rainwater capture and grey water reuse lower municipal water demand.
Urban planning that applies Eco Design promotes mixed use neighborhoods compact development and abundant public space. Together these choices reduce transportation burden and foster active lifestyles. Green corridors and urban forestry improve air quality and biodiversity while cooling cities during heat events.
Real world demonstrations of Eco Design in the built environment show that upfront design costs are offset by lower operating expenses and higher occupant satisfaction. Municipalities can adopt codes and incentives to scale these benefits across new developments and retrofits.
Eco Design for Products and Packaging
Product Eco Design focuses on creating items that deliver function with minimal environmental cost. Designers select recyclable metals and biobased polymers evaluate manufacturing footprints and design for disassembly. Packaging Eco Design reduces material use via minimal sizing reusable containers and materials that are easy to sort for recycling.
A strong Eco Design strategy for consumer goods includes modularity so parts can be replaced and upgrades can extend product life. Subscription models and refurbishment programs change ownership patterns and keep materials in active circulation. Companies that adopt these models often discover new revenue streams and stronger customer loyalty.
The Business Case for Eco Design
Eco Design is not only good for the planet it is a sound business strategy. Companies that lead with Eco Design reduce raw material risk lower energy bills and gain marketplace differentiation. Investors increasingly reward firms that can demonstrate strong environmental governance and long term viability.
Operational savings appear in lower production waste better energy management and reduced material inputs. Brand value strengthens when customers perceive real commitment to sustainability. Many global markets now require environmental disclosures and standards. Firms that integrate Eco Design early face lower compliance costs and smoother access to green finance.
Policy and Regulation That Support Eco Design
Public policy can accelerate adoption of Eco Design. Effective measures include extended producer responsibility rules that require manufacturers to plan for end of life management and building codes that mandate basic energy performance. Financial incentives such as tax relief grants and low cost financing for green buildings and product innovation can reduce adoption barriers.
Government procurement that prefers Eco Design products establishes steady demand and helps scale new supply chains. Public standards and labeling programs give consumers clear signals about product performance and durability enabling better market choices.
Technology and Innovation Enablers
Advances in materials science digital tools and manufacturing methods are enabling faster Eco Design adoption. Life cycle assessment software helps teams quantify environmental impacts and compare design options. Additive manufacturing and precision production reduce waste and allow complex forms that save material while improving performance.
Smart sensors and building management tools optimize energy and water use in real time. Circular business models powered by digital tracking ensure parts are recovered and reused efficiently. These innovations make Eco Design both more practical and more cost effective.
How to Start an Eco Design Program
Organizations that want to adopt Eco Design can follow a structured path to build internal capability and deliver measurable results.
1. Set clear goals and metrics that align with corporate strategy and climate targets.
2. Train design teams in life cycle thinking material selection and durability testing.
3. Pilot projects with measurable outcomes to demonstrate cost savings and customer response.
4. Engage suppliers early to secure low impact materials and responsible production.
5. Use life cycle assessment to inform trade offs and ensure decisions yield real environmental benefits.
6. Share outcomes transparently to build stakeholder trust and to attract partners and investors.
Easy wins often include energy efficiency upgrades material substitutions and re packaging initiatives that cost little to implement and generate rapid returns.
Measuring Success in Eco Design
Clear metrics matter. Useful indicators include carbon footprint per unit durability metrics percent of recycled content water intensity and rate of product return for reuse. Tracking performance across the life cycle prevents problem shifting where a gain in one area produces a loss in another.
Third party verification and labeling can provide independent confirmation of claims and increase consumer trust. Many markets now expect rigorous evidence for sustainability statements.
Real World Examples and Case Studies
From small brands to multinational firms Eco Design practices are generating visible impact. Designers who choose low impact materials and modular construction reduce embodied carbon. Retailers that adopt take back programs and refurbishment services increase material circularity. Cities that integrate Eco Design in public projects create resilient healthy communities.
For those who want to stay current with global Eco Design news and case studies a reliable information source is vital. Visit ecoglobalo.com for curated reporting expert analysis and feature stories that track innovations and policy changes across markets.
How Media and Press Can Support Eco Design
Media coverage plays a key role in amplifying successful projects and informing consumers and policymakers. Press distribution platforms and industry outlets help bring attention to Eco Design milestones case studies and product launches. If you need a reliable press resource for distribution and audience reach consider using respected services to connect your stories with global newsrooms and industry editors. For effective press placement and visibility try Newspapersio.com which helps organizations reach targeted media contacts and amplify sustainable innovations.
Future Trends in Eco Design
Looking ahead Eco Design will continue to converge with digital tools and circular economy thinking. Expect wider use of biomaterials improvements in recycling infrastructure and stronger policy alignment to climate goals. Demand from consumers and institutional buyers will push faster material innovation and business model change.
Designers who master system level thinking and measurable environmental performance will lead markets while contributing to healthier ecosystems and communities.
Conclusion
Eco Design is a strategic pathway to align creativity with planetary limits. It offers designers businesses and policymakers a practical toolkit to reduce impacts enhance user value and create resilient economic outcomes. By embedding life cycle thinking choosing low impact materials optimizing energy use and planning for reuse and recycling Eco Design can deliver strong environmental and financial results. Stay informed apply measurable goals and partner across the value chain to scale durable positive change.
For ongoing coverage of Eco Design trends and global sustainability news visit the resource link above and explore case studies that demonstrate what success looks like in practice.